
The goal of this research project was to develop and validate a machine vision inspection (MVI) system to detect and classify multiple faults using a single camera as a sensor. An industrial automated Oring assembly machine that places O-rings on to continuously moving plastic carriers at a rate of over 100 assemblies per minute was modified to serve as the test apparatus. An industrial camera with LED panel lights for illumination was used to acquire videos of the machine’s operation. A programmable logic controller (PLC) with a human-machine interface (HMI) allowed for the generation of faults in a controlled fashion. Three MVI methods, based on computer vision techniques available in the literature, were developed for this application. The methods used features extracted from the videos to classify the machine’s condition.
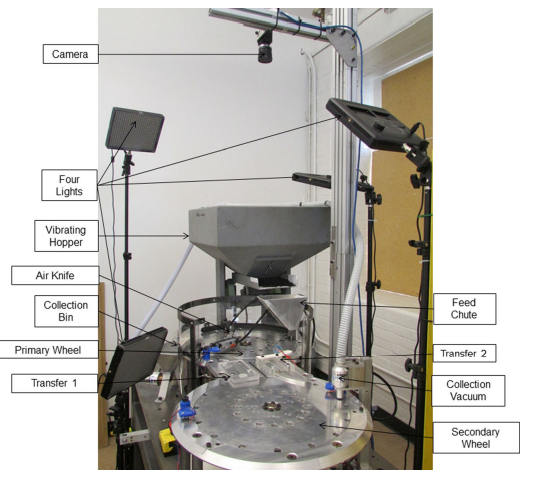
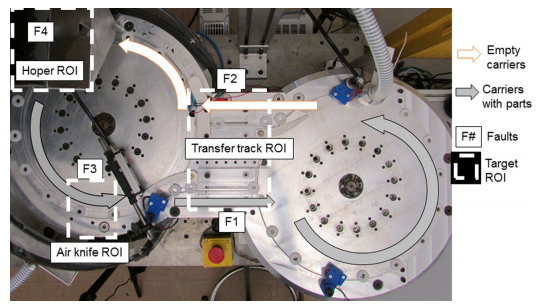
- Continuous operation of an assembly machine results in wear of its various mechanisms that in turn lead to machine faults such as part jams, missing parts in the assembly, misalignments, and blockages with subsequent machine downtime. When machine failure occurs, a small portion of downtime is spent for actual repairing, while the majority of time is consumed in locating the source of the problem.
- MVI systems are popular for finished product inspection applications, robot guidance, object tracing, etc. These systems use industrial grade cameras to acquire data in the form of images and videos. A camera can be used for continuous video acquisition of the machine’s operation and computer vision techniques could be used to develop a fault detection system that is non-intrusive, requires less processing time, and can adapt to changing operating conditions.
- MVI systems are of three types: 1) PC-based, 2) vision sensor-based, and 3) smart camera-based.
1) The PC-based systems use a digital camera that acquires images and sends them to a PC that runs machine vision inspection algorithms. This type of MVI systems is relatively slow due to time required to send image data to the PC.
2) The vision sensor-based systems use a vision sensor that has its own processor and it can do a limited set of predefined inspection tasks. The vision sensor uses proprietary software for application development.
3) The smart camerabased systems use a camera with a processor, memory, digital I/Os, and Ethernet connectivity for remote monitoring and control purposes. The smart camera provides a greater flexibility compared to a vision sensor, and it can do multiple tasks such as image acquisition, processing, and controlling other peripheral systems using its I/Os.
mubnoos
'직업' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 투톤 블로우 (0) | 2021.12.30 |
|---|---|
| AM Project (0) | 2021.11.04 |
| 머신비전을 이용한 업쇼버 로드의 표면검사 시스템 개발 (0) | 2021.07.26 |
| 전동식 다이렉트 블로우 / 라온메카트로닉스 (0) | 2021.07.26 |
| 플라스틱의 구조/성질/결정성 (0) | 2021.06.14 |


